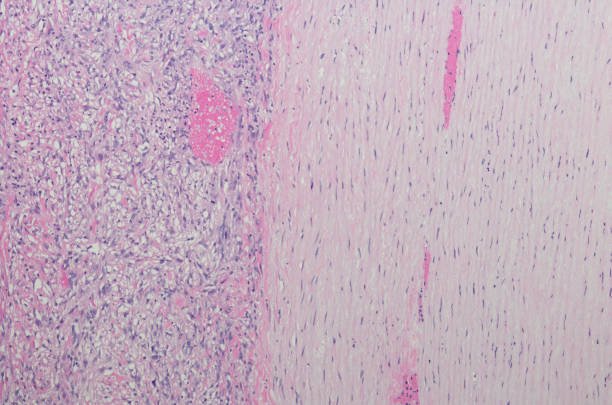
Sarcomatoid mesothelioma is a rare and aggressive form of cancer that affects the mesothelium, a protective lining covering various organs in the body. This article aims to provide an in-depth understanding of sarcomatoid mesothelioma, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, prognosis, coping strategies, prevention, and more. If you or someone you know is affected by this condition, read on to learn valuable insights and important information.
1. Introduction
Cancer, in all its forms, can be devastating, and sarcomatoid mesothelioma is no exception. This article aims to shed light on this rare cancer, helping individuals and families affected by it to better comprehend the condition and explore possible avenues for treatment and care.
2. What is Sarcomatoid Mesothelioma?
At its core, sarcomatoid mesothelioma is an aggressive and malignant tumor that primarily affects the mesothelial cells, which form the protective lining covering organs such as the lungs, heart, abdominal cavity, and others. Often associated with asbestos exposure, this cancer accounts for a small percentage of all mesothelioma cases, making it particularly challenging to diagnose and treat.
3. Causes and Risk Factors
The primary cause of sarcomatoid mesothelioma is exposure to asbestos, a mineral commonly used in construction and industrial materials in the past. Due to its remarkable heat resistance and durability, asbestos was widely used until its harmful effects became apparent. Other risk factors for developing sarcomatoid mesothelioma include genetic predisposition and exposure to certain chemicals and radiation.
4. Symptoms and Diagnosis
Early detection is crucial for effectively managing sarcomatoid mesothelioma. However, the condition often remains asymptomatic or shows vague signs in the early stages, leading to delayed diagnosis. It is essential to recognize the potential symptoms and undergo appropriate diagnostic tests for early intervention.
4.1 Early Signs and Symptoms
The early symptoms of sarcomatoid mesothelioma can be nonspecific and easily mistaken for other common ailments. Persistent cough, shortness of breath, chest pain, fatigue, unexplained weight loss, and respiratory difficulties are some early warning signs that warrant medical attention.
4.2 Diagnostic Methods
To confirm a diagnosis of sarcomatoid mesothelioma, various diagnostic techniques are employed. Imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs provide insights into the affected areas, while biopsies involving tissue samples are essential for accurate diagnosis and histological classification.
5. Types of Sarcomatoid Mesothelioma
Sarcomatoid mesothelioma exhibits different subtypes, and the two most prominent forms are epithelioid sarcomatoid mesothelioma and biphasic sarcomatoid mesothelioma. Understanding these subtypes can aid in determining the treatment approach and prognosis.
5.1 Epithelioid Sarcomatoid Mesothelioma
Epithelioid sarcomatoid mesothelioma represents a transitional form that exhibits characteristics of both epithelioid and sarcomatoid mesothelioma. It often presents with a better prognosis and more treatment options compared to the pure sarcomatoid type.
5.2 Biphasic Sarcomatoid Mesothelioma
Biphasic sarcomatoid mesothelioma is characterized by the presence of both sarcomatoid and epithelioid cells. The aggressiveness and prognosis of this type depend on the ratio of these cell types within the tumor.
6. Treatment Options
The management of sarcomatoid mesothelioma usually involves a multidisciplinary approach, tailored to the individual’s specific condition and overall health. Therapy choices might incorporate a medical procedure, radiation treatment, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy. The decision of therapy relies upon variables like the phase of the disease, generally speaking, wellbeing and patient inclinations.
6.1 Surgery
Surgery plays a vital role in the treatment of sarcomatoid mesothelioma, especially if the cancer is localized and hasn’t metastasized extensively. Surgical options may include:
- Cytoreductive surgery: This procedure aims to remove as much of the tumor as possible, potentially improving the effectiveness of other treatment modalities.
- Extrapleural pneumonectomy (EPP): In cases where the tumor affects the lungs, EPP involves the removal of the affected lung, the lining of the lung, the diaphragm, and nearby lymph nodes.
- Pleurectomy/decortication (P/D): This less aggressive surgical procedure involves removing the pleura and any visible tumors, allowing for better symptom management and potentially improving quality of life.
6.2 Radiation Therapy
Radiation treatment utilizes high-energy pillars to target and obliterate malignant growth cells. It is often employed as an adjuvant treatment following surgery or as a palliative measure to alleviate symptoms. The precise administration helps minimize damage to healthy tissues surrounding the tumor site.
6.3 Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy involves the use of powerful drugs to kill or inhibit the growth of cancer cells throughout the body. While some sarcomatoid mesothelioma patients may not respond as well to chemotherapy as other mesothelioma types, it can still be an important part of the treatment plan, either as a primary approach or in combination with other therapies.
6.4 Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy is a creative methodology that saddles the body’s safe framework to battle disease cells. It involves using drugs that enhance the immune response, potentially improving the body’s ability to identify and destroy cancer cells. While still being researched for sarcomatoid mesothelioma, immunotherapy has shown promising results in treating other types of cancer.
7. Prognosis and Survival Rates
Sarcomatoid mesothelioma generally carries a poor prognosis due to its aggressive nature and resistance to conventional treatments. However, every case is unique, and factors such as the stage at diagnosis, overall health, and response to treatment can influence the prognosis. It is important for patients to consult with medical professionals experienced in treating determine the best course of action.
8. Coping with Sarcomatoid Mesothelioma
Receiving a diagnosis of sarcomatoid mesothelioma can be overwhelming for both the patient and their loved ones. It is crucial to address mental and emotional well-being alongside the physical aspects of the disease. Here are a few strategies to cope:
8.1 Emotional Support
Seeking emotional support from friends, family, or support groups can provide comfort during the journey. Sharing experiences, worries, and hopes can not only alleviate the emotional burden but also offer practical advice and inspiration from others who have faced similar challenges.
8.2 Palliative Care
For individuals with advanced-stage sarcomatoid mesothelioma, palliative care focuses on symptom management, pain relief, and improving quality of life. Palliative care specialists work in conjunction with the primary medical team to address the physical, emotional, and spiritual needs of patients and their families.
9. Clinical Trials and Research
Clinical trials and ongoing research play a crucial role in advancing our understanding of sarcomatoid mesothelioma and developing new treatment options. Patients may inquire about clinical trials that could offer access to novel therapies not yet widely available.
10. Prevention and Precautions
While sarcomatoid mesothelioma may have no foolproof prevention methods, taking precautions can reduce the risk of exposure to asbestos. Avoiding work environments where asbestos exposure is likely, properly following safety protocols in industries where asbestos remnants still exist, and being mindful of potential asbestos-containing materials during remodeling or renovation work can make a significant difference in preventing future cases.
10.1 Safe Work Practices
If you work in an industry where asbestos exposure is a concern, it is vital to adhere to strict safety guidelines. This includes wearing protective gear, using proper ventilation systems, and following protocols for handling asbestos-containing materials. Employers should also take responsibility for ensuring a safe work environment and providing adequate training to their employees.
10.2 Awareness and Education
Raising awareness about the dangers of asbestos and sarcomatoid mesothelioma is crucial for prevention. Educating individuals about the risks, symptoms, and precautions can help prevent unnecessary exposure and reduce the incidence of this aggressive cancer.
10.3 Regular Health Check-ups
If you have a history of asbestos exposure or believe you may be at risk, it is crucial to undergo regular health check-ups. Monitoring your health and discussing any symptoms or concerns with your healthcare provider can lead to early detection and intervention, increasing the chances of successful treatment.
11. Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the overall prognosis for sarcomatoid mesothelioma?
The overall prognosis for sarcomatoid mesothelioma is generally poor due to its aggressive nature and resistance to conventional treatments. However, individual factors such as the stage of cancer, overall health, and response to treatment can influence prognosis, and it is best to consult with medical professionals experienced in treating mesothelioma for accurate information.
2. Can sarcomatoid mesothelioma be cured?
While sarcomatoid mesothelioma is challenging to cure, advancements in treatment options offer hope. Surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and immunotherapy are used in combination or individually to address the disease. Early detection, personalized treatment plans, and participation in clinical trials can positively impact outcomes.
3. Are there any alternative treatments for sarcomatoid mesothelioma?
While conventional treatments remain the mainstay for sarcomatoid mesothelioma, complementary approaches such as acupuncture, meditation, and dietary supplements may provide support during treatment, but they should not replace evidence-based medical care. It is essential to discuss any alternative treatments with your healthcare team to ensure their compatibility and safety.
4. How common is sarcomatoid mesothelioma?
Sarcomatoid mesothelioma is relatively rare, accounting for approximately 10-20% of all mesothelioma cases. Compared to other mesothelioma subtypes, it is less common but more aggressive, leading to a challenging prognosis.
5. Can exposure to asbestos be avoided completely?
While it may be challenging to completely avoid exposure to asbestos due to its historical use in various materials, taking precautions can significantly reduce the risk. Being aware of asbestos-containing materials, following safety protocols, and taking appropriate measures in high-risk environments are essential steps in minimizing exposure.
In conclusion, sarcomatoid mesothelioma is a rare and aggressive cancer primarily associated with exposure to asbestos. Early detection, personalized treatment plans, and ongoing research offer hope for improved outcomes. It is crucial to be vigilant about symptoms, adhere to safety precautions, and engage with healthcare professionals specialized in mesothelioma care. By raising awareness and supporting ongoing research efforts, we can strive to mitigate the impact of sarcomatoid mesothelioma on individuals and their families.